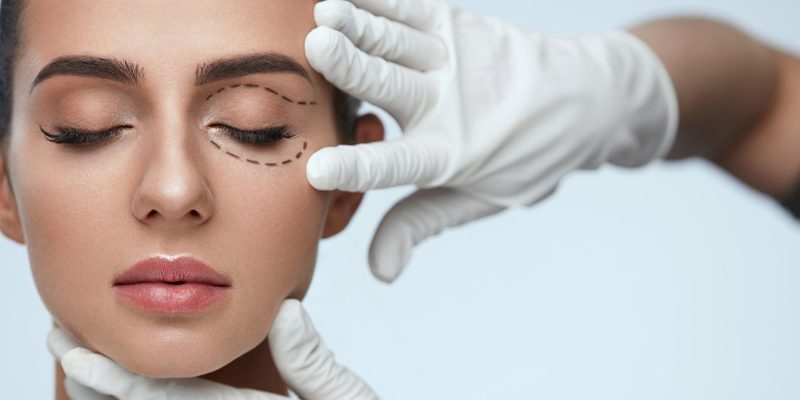
Blepharoplasty is the surgical procedure intended to correct the posture, appearance and function of the eyelids. It can also be performed for both the lower and upper eyelids.
The eyelid skin is one of the thinnest skin areas of the body. With aging, the underlying muscle layer and adipose tissue begin to sag, leading to an unlikeable and tired facial expression.
This sagging also develops in the lower eyelid; and as a result, the under-eye bags in particular become more noticeable. Unfortunately, the progress of this sagging and bad appearance is accelerated by environmental factors (daylight, smoking, etc.) and genetic structure.
Upper and lower blepharoplasty are basically procedures intended to remove the sagging skin and reposition both the muscular tissue and the subcutaneous adipose tissue. After this surgery, the tired and old appearance is dramatically corrected and a rejuvenated appearance is provided in the eye contour area.
Apart from the visual contribution, the procedure is also performed to increase the reduced visual field due to sagging of the upper eyelids, and to prevent eye dryness, infections and disorders such as eye redness caused by droopy lower eyelids.
Blepharoplasty can also be performed in conjunction with other surgical facial rejuvenation procedures (such as brow lift and face lift).
Performance and Postoperative Period of the Surgical Procedure
Upper blepharoplasty can be performed under mild sedation or local anesthesia, but lower blepharoplasty can be safer when performed under general anesthesia. The procedure involving both the upper and lower eyelids will totally take about 2 hours.
For the upper eyelid, an incision is made in accordance with the skin fold (line); and for the lower eyelid, an incision is usually made just below the lower eyelash. Besides the removal of the excess skin, fat and muscle tissues can also be removed or replaced when necessary.
The incision site is closed with self-dissolving sutures, which do not need to be removed. There may be slight redness and bruising around the eyes for a period of time ranging from 7 to 10 days depending on the condition of the person.
In this period, the patient should protect his/her eyes with eye drops and certain creams. Applying cold compresses to the eyes and keeping the head up in the first postoperative days will prevent excessive swelling and bruising.
In the first 10 postoperative days, the patient should avoid activities that can increase the dryness in eyes, such as reading books, using a computer, and watching TV. The patient can usually return to work after the first 7-10 postoperative days.